PERFECTSIGHT's Rare Earth Coating Eye Protection Technology
Most blue light screen protectors on the market filter only 30-40% of the most harmful blue light. PERFECTSIGHT, however, achieves at least 55% filtration. How is this achieved? Let's explore PERFECTSIGHT's proprietary rare earth coating technology for blue light eye protection.
The rare earth coating technology for blue light protection is inspired by the radar wave absorption principles used in the F-22 stealth fighter. Leveraging the properties of multi-layer rare earth composite materials, it absorbs electromagnetic waves (including radar and blue light in the visible spectrum) to provide effective protection. This technology can absorb and block harmful rays, which is why it has been adapted into medical-grade eye-protection screens to shield users' eyes from harmful radiation emitted by screens.
Technical Principles
Selection of Rare Earth Materials: Rare earth elements such as cerium, europium, and neodymium exhibit excellent wave absorption properties. These elements effectively interact with electromagnetic waves (including blue light and UV rays) to absorb and reduce these wavelengths. Rare earth materials maintain high light transmittance, ensuring clear visual quality while absorbing harmful wavelengths.
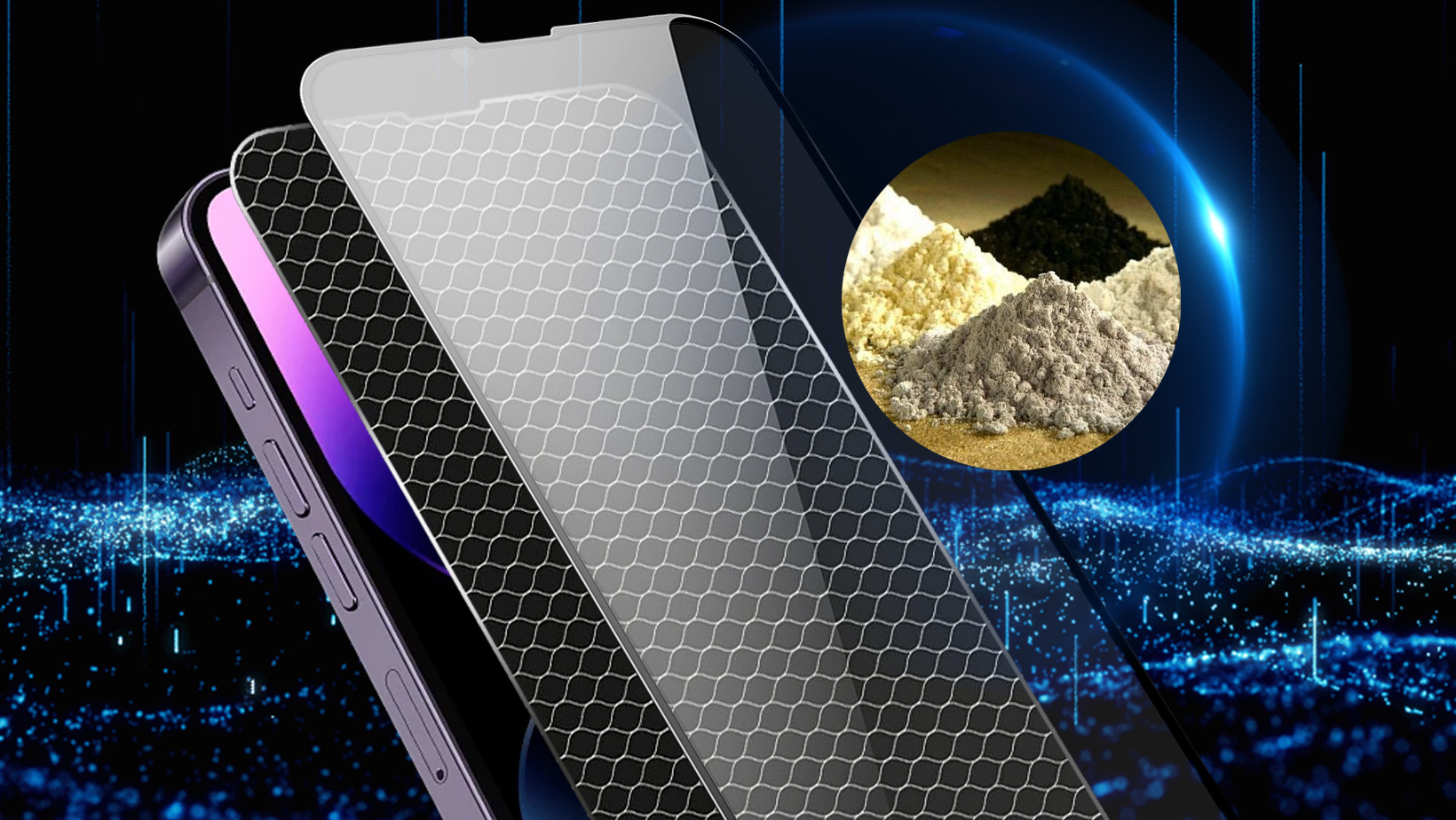

Coating Process
Vacuum Deposition: This process occurs in a vacuum environment where rare earth materials are heated until they vaporize or sublimate, then condense onto the substrate’s surface, forming a very thin layer.
Advantages of this coating technology include:
High Adhesion: The vacuum environment reduces oxidation, enhancing the bond between the coating and the substrate.
Uniformity: Rare earth materials evaporate evenly in the vacuum, forming a smooth, consistent coating without bubbles or particles.
Functional Protection: The coating not only reduces blue light but also blocks other harmful radiation (such as UV and infrared rays), enhancing the protective capabilities of the screen.

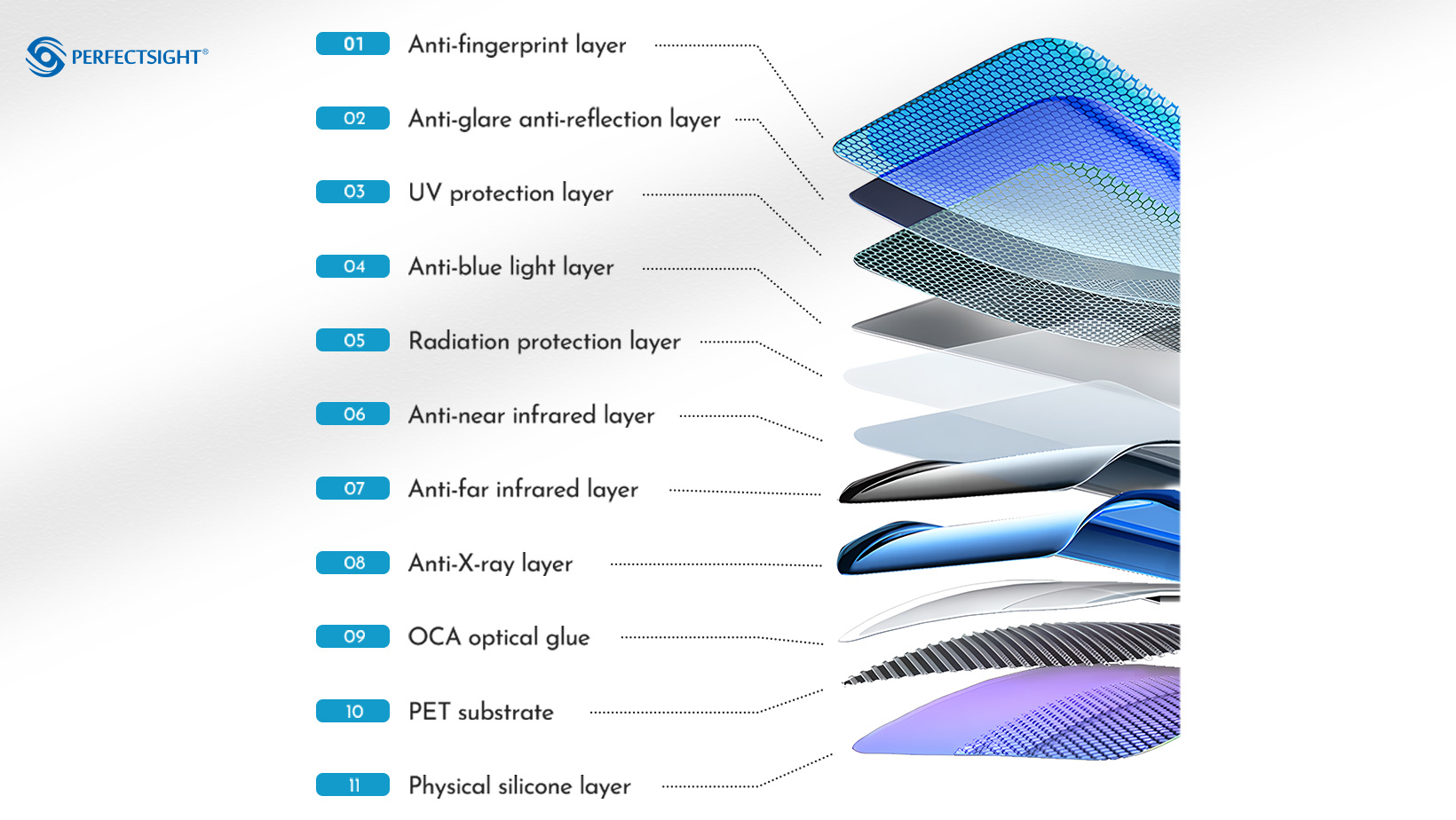
Structure and Performance
Multi-layer Coating Structure: Screen protectors using this technology often feature several layers with distinct functions:
Outer Protective Layer: Made of polymer materials, this layer resists scratches, fingerprints, and other external damage.
Central Rare Earth Absorption Layer: The core layer, responsible for absorbing and reducing blue light and other harmful radiation.
Base Layer: A transparent support substrate, providing stability and maintaining light transmittance across the protector.